Description
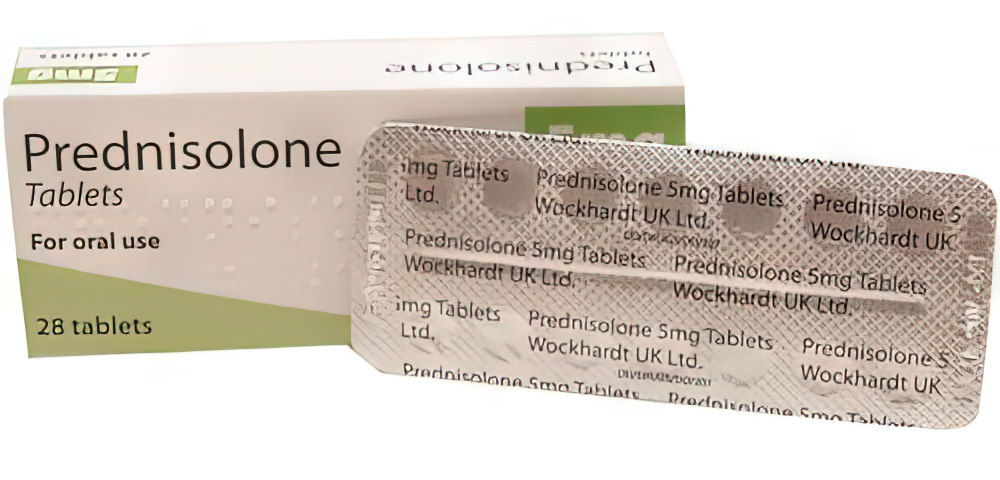
Buy Prednisolone 5 mg tablets
Description of Prednisolone 5 mg tablets:
Prednisolone tablets 5 mg is a steroid medicine. It is used to treat allergic conditions, auto-immune disorders, asthma, skin allergies etc. Prednisolone tablets 5 mg contains prednisolone as its active ingredient. Take the medicine exactly as told by the doctor. Do not miss any dose or stop taking it without consulting the doctor. You must complete the entire course with the medicine. Before initiating treatment with Prednisolone tablets 5 mg, inform the doctor if you are pregnant, planning a pregnancy or breastfeeding and about your detailed medical history.
Prednisolone is available as tablets and as a liquid to drink. It can also be given by injection but this is usually only done in hospital.
Tablets of white color, flat cylindrical shape with a chamfer.
Ingredients of Prednisolone 5 mg tablets:
Active ingredient: prednisolone. 1 tablet contains prednisolone 5 mg;
Excipients: lactose monohydrate, potato starch, calcium stearate.
Pharmacologial Properties of Prednisolone 5 mg tablets:
Pharmacodynamic:
Prednisolone is a dehydrated analogue of hydrocortisone. It has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, desensitizing, anti-shock and immunosuppressive effects. When using prednisolone, the effects of the drug are realized through the stabilization of cell membranes, inhibition of the accumulation of macrophages, a decrease in the migration of leukocytes, and a decrease in capillary permeability, which prevents the formation of edema. Prednisolone inhibits phagocytosis, affects the metabolism of arachidonic acid, as well as the synthesis and release of inflammatory mediators. The immunosuppressive effect of prednisolone is due to inhibition of the activity of T- and B-lymphocytes, a decrease in the complement content in the blood, as well as inhibition of the production and effects of interleukin-2. Shows a catabolic effect, increases the level of glucose in the blood. It shows some mineralocorticoid activity, increases the reabsorption of Na + and water in the renal tubules, increases the excretion of K + and Ca + from the body, especially with an increase in their level in blood plasma. Prednisolone inhibits the synthesis and secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormones by the pituitary gland and, secondarily, glucocorticosteroids by the adrenal glands.
Pharmacokinetic:
Rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Has high bioavailability. The time to reach maximum plasma concentration is 1-1.5 hours. Most of the drug (90%) binds cortisone-binding globulin – transcortin and albumin. Metabolized in the liver, kidneys, small intestine, bronchi. Oxidized forms of prednisolone are glucuronidated or sulfated. The half-life (T1 / 2) is 2-4 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys mainly in the form of metabolites, up to 20% unchanged.
Indication of Prednisolone 5 mg tablets :
Contraindications of Prednisolone 5 mg tablets :
Interaction with other medicinal products:
With the simultaneous use of prednisolone with other drugs, it is possible:
- with thyroid hormones, inducers of liver enzymes, in particular with barbiturates, phenytoin, pyrimidone, carbamazepine, rifampicin – a weakening of the effects of prednisolone as a result of an increase in its systemic clearance;
- with estrogens (including oral contraceptives, which include estrogen), cyclosporine, CYP3A4 inhibitors, in particular erythromycin, clarithromycin, ketoconazole, diltiazem, aprepitant, itraconazole, oleandomycin – increased therapeutic and toxic effects of prednisolone;
- with antacids – reduced absorption of prednisolone;
- with derivatives of salicylic acid and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs – an increase in the likelihood of ulceration of the gastric mucosa; prednisolone reduces the level of salicylic acid derivatives in the blood serum, increasing their renal clearance; the drug increases the risk of developing hepatotoxic reactions of paracetamol as a result of the induction of liver enzymes and the formation of its toxic metabolite;
- with cardiac glycosides – increased toxicity of the latter, and as a result of the resulting hypokalemia – an increased risk of developing arrhythmias;
- with hypoglycemic agents – suppression of the hypoglycemic effect of oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin;
- with antihypertensive drugs – a decrease in the effectiveness of the latter;
- with tricyclic antidepressants – increased signs of depression caused by taking prednisolone, and increased intraocular pressure;
- with immunosuppressants – an increased risk of developing infections and lymphoma or other lymphoproliferative disorders associated with the Epstein-Barr virus;
- with diuretics, laxatives, amphotericin B – increased risk of hypokalemia; prednisolone increases the risk of developing osteoporosis when used simultaneously with amphotericin and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors;
- with m-anticholinergics, antihistamines, nitrates – an increase in intraocular pressure and a decrease in the effectiveness of antihistamines;
- with antipsychotics, carbutamide, azathioprine – an increased risk of developing cataracts;
- with estrogens, anabolic drugs, oral contraceptives – manifestations of hirsutism and acne;
- with live antiviral vaccines and against the background of other types of immunizations – an increase in the risk of activation of viruses and the development of infections;
- with muscle relaxants against the background of hypokalemia – increased signs and duration of muscle blockade against the background of the use of muscle relaxants;
- with anticholinesterase agents – the occurrence of muscle weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis (especially in patients with myasthenia gravis);
- with mitotane and other inhibitors of the function of the adrenal cortex – may cause an increase in the dose of the drug;
- with antiemetics – increased antiemetic effect;
- with isoniazid, mexiletine, praziquantel – a decrease in their plasma concentrations;
- with somatotropin (in high doses) – a decrease in the effect of the latter;
- with fluoroquinolones – tendon damage;
- with cyclosporine – there have been cases of seizures. Since the simultaneous administration of these drugs causes mutual inhibition of metabolism, it is likely that convulsions and other side effects associated with the use of each of these drugs, both in monotherapy and in their combined use, may occur more often. Co-administration may cause an increase in plasma concentrations of other medicinal products.
With long-term therapy, prednisolone increases the content of folic acid.
Precautions and Warnings of Prednisolone 5 mg tablets :
Before starting treatment, the patient must be examined to identify possible contraindications. Clinical examination should include examination of the cardiovascular system, X-ray examination of the lungs, examination of the stomach and duodenum; urinary system, organs of vision. Laboratory examination should include: a complete blood count, the concentration of glucose in the blood and urine, electrolytes in the blood plasma.
When treating with glucocorticoids for a long time, it is recommended to regularly monitor blood pressure, determine the level of glucose in urine and blood, conduct a fecal occult blood test, blood coagulation tests, X-ray control of the spine, ophthalmological examination (1 time in 3 months).
Children who during the period of treatment were in contact with patients with measles or chicken pox should be given specific immunoglobulins as a prophylaxis (within 10 days after contact).
During treatment should not be immunized.
If unusual stress situations occur in patients during treatment with glucocorticoids, it is recommended to increase the dose of fast-acting corticosteroids before, during and after the stressful situation.
Alcohol should not be consumed during treatment with prednisone.
Depending on the duration of treatment and dose, a negative effect of the drug on calcium metabolism is possible. Prevention of osteoporosis is recommended, which is especially important in patients with risk factors (including family history, older age, postmenopause, insufficient protein and calcium intake, excessive smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and decreased physical activity). Prevention is based on an adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, and also includes physical activity.
To reduce the side effects of prednisolone therapy, it is justified to prescribe an appropriate diet.
When using high doses of prednisolone for a long period (30 mg per day for at least 4 weeks), reversible disorders of spermatogenesis may occur, which persist for several months after discontinuation of the drug.
In patients who have received higher than physiological doses of prednisolone (approximately 7.5 mg prednisolone or equivalent) for more than 3 weeks, stop prednisolone treatment gradually. Treatment should be stopped gradually, even if it lasted less than 3 weeks, in such groups of patients:
- patients undergoing a second course of treatment with prednisolone;
- patients who received a second course of treatment within a year after long-term treatment (months, years);
- patients receiving more than 40 mg per day of prednisolone or equivalent;
- patients with adrenal insufficiency not caused by exogenous corticosteroids.
After discontinuation of treatment, withdrawal syndrome, adrenal insufficiency, as well as an exacerbation of the disease, for which prednisolone was prescribed, may occur. If functional adrenal insufficiency is observed after the end of treatment with prednisolone, the drug should be resumed immediately, and the dose reduction should be carried out very slowly and with caution (for example, the daily dose should be reduced by 2-3 mg for 7-10 days).
Atrophy of the adrenal cortex develops with prolonged therapy and may persist for many years after discontinuation of treatment.
Steroid-induced secondary adrenal insufficiency can be reduced to a minimum as a result of gradual dose reduction. This type of insufficiency may persist for several months after the end of therapy, therefore, in case of any stressful situation that has arisen during this period, it is necessary to resume corticosteroid therapy.
With sudden withdrawal, especially in the case of previous use of high doses, a withdrawal syndrome occurs, which is manifested by fever, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, lethargy, dizziness, generalized musculoskeletal pain, asthenia.
Because of the risk of developing hypercortisolism, a new course of cortisone treatment after a previous long-term treatment with prednisolone for several months should always be started at low initial doses (except in acute life-threatening conditions).
In children during the period of growth, glucocorticosteroids can be used only according to absolute indications and under the most careful supervision of a physician.
With intercurrent infections, septic conditions and tuberculosis, simultaneous antibiotic therapy is necessary.
If it is necessary to use prednisolone while taking oral hypoglycemic drugs or anticoagulants, it is necessary to adjust the dosing regimen of the latter.
The electrolyte balance should be especially carefully monitored when prednisone is used in combination with diuretics. With long-term treatment with prednisone, in order to prevent hypokalemia, it is necessary to prescribe potassium drugs and an appropriate diet due to a possible increase in intraocular pressure and the development of subcapsular cataracts.
Use in severe infectious diseases is permissible only against the background of specific antimicrobial therapy.
Women during menopause should be tested for the possibility of osteoporosis.
In Addison’s disease, the simultaneous administration of barbiturates should be avoided due to the risk of developing acute adrenal insufficiency (Addisonian crisis).
If there is a history of psoriasis, convulsions, prednisolone should be used only in the minimum effective doses.
With extreme caution, the drug should be used for liver and kidney failure, migraine.
Particular attention should be paid to the use of systemic corticosteroids in patients with existing or history of severe affective disorders, which include depressive, manic-depressive psychosis, previous steroid psychosis. Patients and/or caregivers should be warned about the possibility of serious psychiatric side effects. Symptoms usually appear within a few days or weeks after starting treatment. The risk of these side effects is higher at higher doses. Most reactions disappear after dose reduction or drug withdrawal, although specific treatment is sometimes necessary. With the development of such symptoms, you should consult a doctor. Also, mental disorders can be observed during the withdrawal of glucocorticoids.
Use during pregnancy or lactation.
Controlled studies in pregnant women have not been conducted. During pregnancy (especially in the Ι trimester), use is possible if the benefit to the mother outweighs the risk to the fetus. When using the drug during breastfeeding, it should be remembered that prednisone passes into breast milk.
The ability to influence the reaction rate when driving vehicles or operating other mechanisms.
During the period of treatment, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require an increased concentration of attention and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Overdose:
The risk of overdose increases with prolonged use of the drug, especially at high doses.
Symptoms: increased blood pressure, peripheral edema, increased side effects.
Treatment of acute overdose: immediate gastric lavage or induction of vomiting. There is no specific antidote.
Treatment of chronic overdose: reduction of the dose of the drug.
Side Effects:
The frequency of development and severity of side effects depend on the duration of use, the size of the dose used and the possibility of observing the circadian rhythm of the appointment.
On the part of the organs of vision: glaucoma, papilledema, cataracts, posterior subcapsular cataracts, increased intraocular pressure with possible damage to the optic nerve, a tendency to develop secondary bacterial, fungal or viral eye infections, trophic changes in the cornea, exophthalmos.
From the gastrointestinal tract: an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth, dyspepsia, esophageal candidiasis, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, diarrhea, pancreatitis, “steroid” gastric and duodenal ulcers, erosive esophagitis, bleeding and perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, increased or decreased appetite, flatulence, hiccups. In rare cases, an increase in the activity of “liver” transaminases and alkaline phosphatase.
From the side of the kidneys and urinary system: increased risk of urates, uroliths, an increase in the number of leukocytes and erythrocytes in the urine without a clear violation of the kidneys, leukocyturia.
From the endocrine system: increased need for insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs, hyperlipidemia, postmenopausal bleeding, decreased glucose tolerance, “steroid” diabetes mellitus or manifestation of latent diabetes mellitus, depression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system, menstrual disorders, growth retardation in children and adolescents, delayed sexual development in children, Itsenko-Cushing’s syndrome (moon-shaped face, pituitary-type obesity, hirsutism, increased blood pressure, dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, myasthenia gravis, striae).
On the part of metabolism, metabolism: violation of the mineral and electrolyte balance, hypocalcemia, negative nitrogen balance (increased protein breakdown), weight gain. Side effects due to the glucocorticosteroid activity of prednisolone: fluid retention and Na + (peripheral edema), hypernatremia, hypokalemic syndrome – arrhythmia, myalgia or muscle spasm, unusual weakness and fatigue.
From the nervous system: peripheral neuropathy, paresthesia, autonomic disorders, headache, dizziness, cerebellar pseudotumor, increased intracranial pressure, convulsions.
On the part of the psyche: irritability, sleep disturbance, euphobia, suicidal tendencies, increased concentration, psychological dependence, mania, exacerbation of schizophrenia, dementia, psychosis, epileptic seizures, cognitive dysfunction (including amnesia and impaired consciousness), delirium, disorientation, euphoria, hallucinations , manic-depressive psychosis, depression, paranoia, nervousness, anxiety, insomnia.
From the side of the cardiovascular system: arterial hypotension, atherosclerosis, thrombosis, vasculitis, peripheral edema, arrhythmia, bradycardia, arterial hypertension, development or increase in manifestations of chronic heart failure, ECG changes characteristic of hypokalemia. In patients with acute and subacute myocardial infarction – the spread of necrosis, slowing down the formation of scar tissue, which can lead to rupture of the heart muscle.
On the part of the blood and lymphatic system: an increase in the total number of leukocytes with a decrease in the number of eosinophils, monocytes and lymphocytes. The mass of lymphoid tissue decreases. Leukocyturia, hypercoagulability leading to thrombosis and thromboembolism.
From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, itching, hyperemia, urticaria, Quincke’s edema, anaphylactic shock.
On the part of the skin and subcutaneous tissue: skin atrophy, telangiectasia, acne, hirsutism, purpura, poststeroid paniculitis, which is characterized by the appearance of erythematosis, hot subcutaneous thickening within 2 weeks after discontinuation of the drug, Kaposi’s sarcoma, slowing down the regeneration process, petechiae, bruises, hematomas , ecchymosis, striae, thinning of the skin, hyper- or hypopigmentation, acne, a tendency to develop pyoderma.
From the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue: growth retardation and ossification processes in children (premature closure of epiphyseal growth zones), osteoporosis, very rarely – pathological bone fractures, aseptic necrosis of the head of the humerus or femur, muscle tendon rupture, “steroid” myopathy a decrease in muscle mass (atrophy).
Infections and invasions: masking the symptoms of bacterial, viral, fungal infections, opportunistic infections, reducing the body’s resistance to infections.
General disorders and reactions at the injection site: withdrawal syndrome, edema, aphthous ulcers, malaise, persistent hiccups when using the drug in high doses; insufficiency of the adrenal glands, which leads to arterial hypotension; hypoglycemia and deaths in stressful situations such as surgery, trauma or infection if the dose of prednisolone is not increased.
With a sudden withdrawal of the drug, a withdrawal syndrome is possible, the severity of symptoms depends on the degree of atrophy of the adrenal glands, headache, nausea, abdominal pain, dizziness, anorexia, weakness, mood changes, lethargy, fever, myalgia, arthralgia, rhinitis, conjunctivitis, painful itching of the skin, weight loss. In more severe cases, severe mental disorders and increased intracranial pressure, steroid pseudorheumatism in patients with rheumatism, and deaths.
Storage:
Store in original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life:
3 year.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.