Description
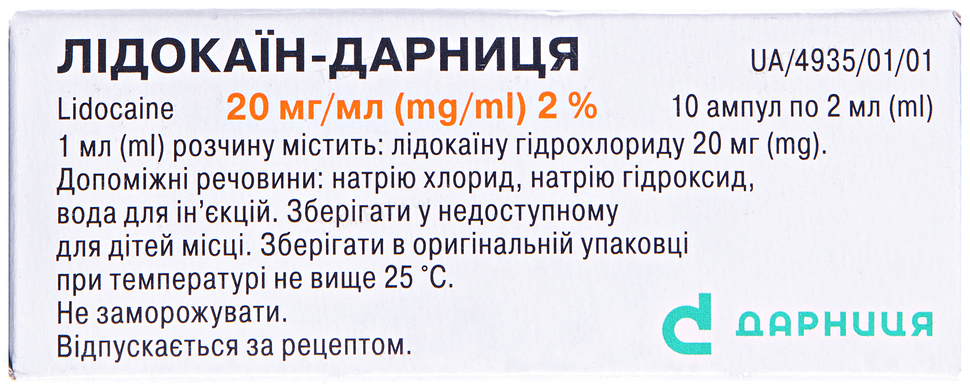
Buy Lidocaine Solution for injection 20 mg/ml 2 ml #10
Description of Lidocaine Solution for injection 20 mg/ml 2 ml:
Local anesthetic for terminal, infiltration, conduction anesthesia. The relative toxicity of lidocaine hydrochloride depends on the concentration of the solution.
Ingredients:
Active ingredient: lidocaine. 1 ml of solution contains lidocaine hydrochloride 20 mg;
Excipients: sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide, water for injection.
Pharmacodynamics of Lidocaine Solution for injection 20 mg/ml 2 ml:
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic. The local anesthetic effect is due to the stabilization of the neuronal membrane by reducing its permeability to sodium ions, which prevents the occurrence of an action potential and the conduction of nerve impulses. Antagonism with calcium ions is possible. Effective for all types of local anesthesia. It inhibits the conduction of not only pain impulses, but also impulses of a different modality. It is quickly hydrolyzed in the slightly alkaline environment of tissues and after a short latent period it acts for 1-1.5 hours. The anesthetic effect of lidocaine is 2-6 times stronger than procaine. With inflammation, anesthetic activity decreases. When applied topically, it dilates blood vessels, does not have a local irritating effect.
Pharmacokinetics of Lidocaine Solution for injection 20 mg/ml 2 ml:
When applied topically to mucous membranes, lidocaine is absorbed to varying degrees depending on the dose and site of application (maximum concentration is reached after 10-20 minutes); absorption is affected by the rate of perfusion through the mucosa. With intramuscular injection, the maximum concentration is reached after 5-15 minutes. Plasma protein binding – 60-80% (depending on the dose).
Easily passes through histohematic barriers, including the blood-brain barrier. First, it enters tissues with good blood supply (heart, lungs, brain, liver, spleen), then – into adipose and muscle tissues. Penetrates through the placenta, in the body of the newborn, 40-55% of the concentration of the drug administered to the woman in labor is detected.
It is metabolized by 90% in the liver by oxidative N-dealkylation with the formation of active metabolites: monoethylglycine xylidine and glycine xylidine, which have half-lives of 2 and 10 hours, respectively. Shows the effect of “first pass”.
With impaired liver function, the half-life may increase by more than 2 times. 5-20% is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Warnings and Application Features for use of Lidocaine Solution for injection 20 mg/ml 2 ml:
The introduction of lidocaine can only be carried out by medical professionals.
When treating the injection site with disinfectants containing heavy metals, the risk of developing a local reaction in the form of pain and swelling increases.
When using lidocaine, ECG monitoring is mandatory. In case of violations of the activity of the sinus node, prolongation of the P-Q interval, expansion of the QRS, or the development of a new arrhythmia, the dose should be reduced or the drug should be discontinued.
Before using lidocaine in heart disease (hypokalemia reduces the effectiveness of lidocaine), it is necessary to normalize the level of potassium in the blood.
Before the introduction of lidocaine in high doses, the appointment of barbiturates is recommended. When conducting planned subarachnoid anesthesia, it is necessary to cancel MAO inhibitors no later than 10 days before anesthesia.
Care should be taken to avoid accidental intravasal (especially when performing local anesthesia in areas containing many blood vessels) or subdural administration of the drug. It is necessary to establish careful monitoring of the systemic toxic effect of the drug on the cardiovascular and central nervous system (since the doses intended for epidural anesthesia are always higher than for subdural anesthesia); When injected into vascularized tissues, an aspiration test is recommended.
Caution should be exercised when anesthesia around the spinal region for patients with neurological diseases, spinal deformity, septicemia and severe hypertension.
Smaller doses should be administered to the head and neck, including retrobulbar and dental administration, as well as use for blockade of the stellate ganglion, since the systemic toxic effects of the drug through retrograde flow can enter the cerebral circulation.
Extreme caution should be observed with retrobulbar administration, since side effects are possible: collapse, shortness of breath, convulsions, reversible blindness.
Since lidocaine has a pronounced antiarrhythmic effect and can itself act as an arrhythmogenic factor, which can cause the development of arrhythmias, it is necessary to collect an anamnesis before administering the drug and use the drug with caution in people with complaints of arrhythmias in the past.
Use with caution and in smaller doses in patients with moderate heart failure, moderate arterial hypotension, incomplete AV blockade, impaired intraventricular conduction, impaired liver and kidney function of moderate degree (creatinine clearance of at least 10 ml / min, epilepsy, after heart surgery , with a genetic predisposition to malignant hyperthermia, debilitated patients and elderly patients.
With intramuscular administration of lidocaine, the concentration of creatinine may increase, which can lead to an error in the diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction.
With local anesthesia of tissues with severe vascularization (for example, the neck during thyroid surgery), special care should be taken to avoid getting the drug into the vessels.
The safety of amide group anesthetics is questionable in patients prone to malignant hyperthermia, so their use in such cases should be avoided.
Special care should be taken when using lidocaine in patients with circulatory failure, hypovolemia, arterial hypotension, hepatic and renal insufficiency.
Use with caution in patients with disorders of the central nervous system who use drugs, as sudden side effects from the cardiovascular system may occur. With prolonged use, the level of electrolytes in the blood should be monitored. Use with caution in patients with a tendency to convulsions, in a state of shock, with hypoxia.
This medicinal product contains 6 mg/ml sodium chloride, i. e. practically free of sodium.
Use during pregnancy or lactation
The drug crosses the placental barrier and can cause fetal bradycardia, so it is not recommended to prescribe it during pregnancy. If necessary, the use of the drug breast-feeding should be discontinued.
The ability to influence the reaction rate when driving vehicles or operating other mechanisms
The drug affects the function of the central nervous system, therefore, after using lidocaine, it is not recommended to drive vehicles or work with other mechanisms.
Indications for use of Lidocaine Solution for injection 20 mg/ml 2 ml:
Local anesthesia (terminal, infiltration, conduction) in surgery, ophthalmology, dentistry, otorhinolaryngology; blockade of peripheral nerves and nerve plexuses in various pain syndromes.
Contraindications of Lidocaine Solution for injection 20 mg/ml 2 ml:
Individual hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, as well as to other amide local anesthetic drugs; a history of epileptoform convulsions associated with the administration of lidocaine hydrochloride; AV block II and III degree, complete transverse heart block; sick sinus syndrome; Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, Adams-Stokes syndrome; severe forms of heart failure (II-III degree); severe arterial hypotension; severe bradycardia; cardiogenic shock; complete transverse heart block; myasthenia gravis; hypovolemia; porphyria; severe renal and / or liver failure; retrobulbar injection in patients with glaucoma; blood coagulation disorders, anticoagulant therapy; infection at the injection site; non-contact patients.
Interactions:
- Chlorpromazine, pethidine, bupivacaine, quinidine, disopyramide, amitriptyline, imipramine, nortriptyline – when combined with lidocaine, the concentration of the latter in the blood plasma decreases;
- Antiarrhythmic drugs (including amiodarone, verapamil, quinidine, disopyramide, aimaline) – when combined with lidocaine, the cardiodepressive effect is enhanced, in particular, the QT interval is prolonged and, in isolated cases, AV blockade or ventricular fibrillation may develop. Simultaneous use with amiodarone may lead to the development of seizures;
- Procainamide – when combined with lidocaine, delirium, hallucinations are possible;
- Novocain, novocainamide – when combined with lidocaine, excitation of the central nervous system, hallucinations is possible;
- Curare-like drugs – when combined with lidocaine, muscle relaxation increases (paralysis of the respiratory muscles is possible);
- Ethanol – when combined with lidocaine, it enhances the inhibitory effect of the latter on breathing;
- Vasoconstrictors (epinephrine, methoxamine, phenylephrine) – when combined with lidocaine, they slow down the absorption of lidocaine and prolong the effect of the latter;
- Cimetidine – when used in combination, it reduces the hepatic clearance of lidocaine (decrease in metabolism as a result of inhibition of microsomal oxidation) and increases its concentration and the risk of developing toxic effects;
- Guanadrel, guanethidine, mecamylamine, trimethaphan – when combined for spinal and epidural anesthesia with lidocaine, the risk of severe hypotension and bradycardia increases;
- β-blockers – when used in combination, they slow down the metabolism of lidocaine in the liver, the effects of lidocaine (including toxic ones) are enhanced, and the risk of developing bradycardia and arterial hypotension increases. With the simultaneous use of β-blockers and lidocaine, it is necessary to reduce the dose of the latter;
- Cardiac glycosides – when combined with lidocaine, the cardiotonic effect of cardiac glycosides is weakened;
- Digitalis glycosides – against the background of intoxication, lidocaine can increase the severity of AV blockade;
- Hypnotics or sedatives – when combined with lidocaine, it is possible to increase the inhibitory effect on the central nervous system of hypnotics and sedatives;
- Narcotic analgesics (morphine) – when combined with lidocaine, the analgesic effect of narcotic analgesics increases, but respiratory depression also increases;
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (furazolidone, procarbazine, selegiline) – when combined with lidocaine, the risk of arterial hypotension increases and the local anesthetic effect of the latter is prolonged. During treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, parenteral lidocaine should not be used;
- Anticoagulants (including ardeparin, dalteparin, danaparoid, enoxaparin, heparin, warfarin) – when combined with lidocaine, the risk of bleeding increases;
- Anesthesia drugs – when combined with lidocaine, the latter enhances the inhibitory effect on the respiratory center of anesthesia drugs (hexobarbital, sodium thiopental intravenously);
- Polymyxin B – when combined with lidocaine, control of respiratory function is necessary;
- Rifampicin – when combined with lidocaine, a decrease in the concentration of the latter in the blood is possible;
- Propafenone – when combined with lidocaine, an increase in the duration and severity of side effects from the central nervous system is possible;
- Prenylamine – when combined with lidocaine, the risk of developing ventricular arrhythmia of the “pirouette” type increases;
- Anticonvulsants, barbiturates (phenytoin) – when combined with lidocaine, it is possible to accelerate the metabolism of lidocaine in the liver, reduce blood concentrations, increase the cardiodepressive effect;
- Isadrin, glucagon – when combined with lidocaine, the clearance of lidocaine increases;
- Norepinephrine, mexiletine – when combined with lidocaine, the clearance of the latter decreases (toxicity increases); decreased hepatic blood flow;
- Acetazolamide, thiazide and loop diuretics – when combined with lidocaine, as a result of creating hypokalemia, reduce the effect of the latter;
- Midazolam – when combined with lidocaine, the concentration of the latter in the blood plasma increases;
- Drugs that block neuromuscular transmission – when combined with lidocaine, the effect of drugs that block neuromuscular transmission is enhanced, since the latter reduce the conduction of nerve impulses.
Overdose of Lidocaine Solution for injection 20 mg/ml 2 ml:
May increase adverse reactions.
Symptoms: psychomotor agitation, dizziness, general weakness, decreased blood pressure, tremor, blurred vision, tonic-clonic convulsions, coma, collapse, AV blockade, asphyxia, apnea. The first symptoms of overdose in healthy volunteers occur when the concentration of lidocaine in the blood is more than 0.006 mg / kg, convulsions – at 0.01 mg / kg.
Treatment: discontinuation of the drug, oxygen therapy, anticonvulsants, vasoconstrictors (norepinephrine, mezaton), anticholinergics. The patient should be in a horizontal position; it is necessary to provide access to fresh air, oxygen supply and / or artificial respiration. CNS symptoms are corrected with short-acting benzodiazepines/barbiturates. If an overdose occurs during anesthesia, a short-term muscle relaxant should be used. To correct bradycardia and conduction disturbances, atropine (0.5-1 mg intravenously) is used, with arterial hypotension – sympathomimetics in combination with β-adrenergic receptor agonists. In case of cardiac arrest, immediate resuscitation is indicated. It is possible to carry out intubation, artificial ventilation of the lungs. In the acute phase of overdose, dialysis is ineffective. There is no specific antidote.
Side effects:
When using the drug, side reactions are possible:
- on the part of the cardiovascular system: lowering blood pressure, tachycardia – when administered with a vasoconstrictor, bradycardia, peripheral vasodilation, collapse, tachycardia, palpitations, chest pain, heart pain, arrhythmia, slow heart conduction, transverse heart block, fibrillation ventricles, cardiac arrest; very rarely – arterial hypertension;
- from the side of the central and peripheral nervous system: excitation of the central nervous system (when used in high doses), anxiety, dizziness, confusion, drowsiness, sleep disturbance, headache, weakness, restlessness, euphoria, nystagmus, loss of consciousness, impaired sensitivity, paresthesia, numbness of the tongue and lips (when used in dentistry); in patients with hypersensitivity – euphoria, tremor, trismus, muscle twitching, restlessness, convulsions (the risk of their development increases against the background of hypercapnia and acidosis); persistent anesthesia, paresis or elegy of the lower extremities and loss of sphincter control (for example, cauda equina syndrome) – causes more often than other local anesthetics, motor and sensory block, dysarthria, dysphagia, coma;
- on the part of the organs of vision: blurred vision, blurred vision, diplopia, nystagmus, flickering “flies” before the eyes, dilated pupils, photophobia, reversible blindness, conjunctivitis;
- on the part of the hearing organs: hearing impairment, tinnitus, hyperacusis;
- mental disorders: anorexia, irritability, restlessness, hallucinations, depression, anxiety, sleep disturbances, state of agitation;
- on the part of the respiratory system, chest organs and mediastinum: rhinitis, shortness of breath, shortness of breath, feeling of suffocation, respiratory depression, bronchospasm, paralysis of the respiratory muscles, respiratory paralysis (more often develops with subarachnoid anesthesia), respiratory arrest;
- from the digestive tract: nausea, vomiting, involuntary defecation, abdominal pain;
- from the urinary system: involuntary urination;
- on the part of the skin and subcutaneous tissue: hyperemia, itching, rash, urticaria;
- from the reproductive system: decreased libido and / or potency;
- from the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema, generalized exfoliative dermatitis, anaphylactic shock, anaphylactic reactions, suppression of the immune system;
- reactions at the injection site: a slight burning sensation that disappears with the development of an anesthetic effect (within 1 minute), swelling, hyperemia, itching, rash, thrombophlebitis, localized nerve damage at the injection site; with spinal or epidural anesthesia, pain in the back, legs, partial / complete spinal blockade can be observed, which is accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure, impaired defecation, involuntary urination, impotence, loss of sensation in the perineum (the likelihood of these effects increases with high doses or in the case of accidental injection of lidocaine into the spinal space when the dose intended for administration into the epidural space enters the spinal space); in some cases, after such an intervention, the restoration of motor, sensory and / or vegetative function occurs slowly (after a few months) or incompletely;
- general disorders: persistent anesthesia, hypothermia, sensation of heat, cold or numbness of the extremities, malignant hyperthermia, increased sweating, pallor of the skin, edematous syndrome, weakness.
Storage:
Store below 25°C in original packaging. Do not freeze.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life:
3 years.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.