Description
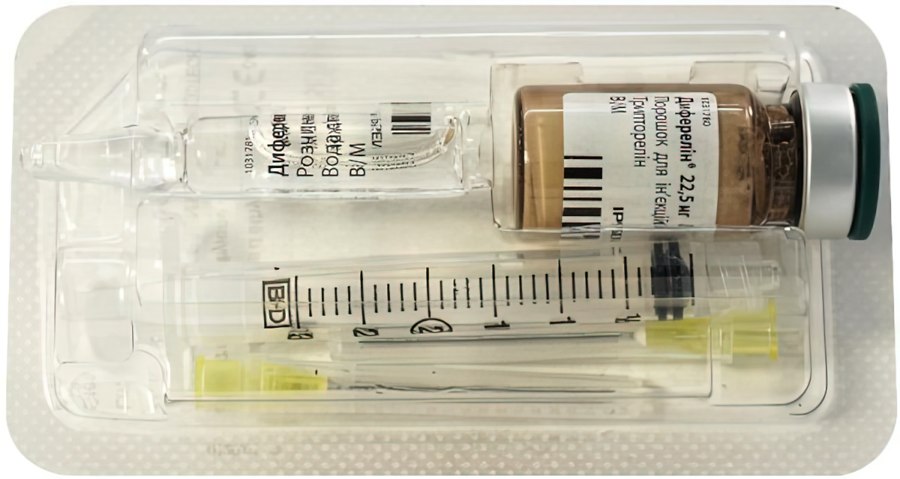
Buy Diphereline Triptorelin 22.50 mg/ml powder with solvent
Description of Diphereline 22.50 mg/ml solution for injection:
Powder and solvent for sustained release injection suspension.
Lyophilisate for the preparation of a suspension for intramuscular administration of a prolonged action of white or white with a creamy tint, dispersible in the attached solvent to form a suspension of white or white with a creamy tint.
powder – freeze-dried mass from white to slightly yellow in brown glass vial with a dark green Flip-offTM plastic cap;
solvent (water for injection) – a clear, colorless solution, practically free of visible particles.
Ingredients:
active ingredient: triptorelin;
1 vial contains triptorelin embonate 31 mg, equivalent to triptorelin 22.5 mg;
other components: poly(dl-lactide coglycolide) 75/25, poly(dl-lactide coglycolide) 85/15, mannitol (E 421), sodium carmellose, polysorbate 80;
solvent: water for injection
Pharmacological Properties of Diphereline 22.50 mg/ml solution for injection:
Pharmacodynamics:
Triptorelin, a GnRH agonist, acts as a potent inhibitor of gonadotropin secretion when administered chronically at therapeutic doses. Studies in humans and animals show that after the administration of triptorelin, there is an initial and transient increase in the levels of circulating luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and testosterone in males/males and estradiol in females/females.
However, prolonged and continuous administration of triptorelin leads to a decrease in the secretion of LH and FSH and inhibition of testicular and ovarian steroidogenesis.
In men with prostate cancer
A decrease in serum testosterone levels to the ranges typically found in men undergoing surgical castration is observed approximately 2 to 4 weeks after initiation of therapy with Diphereline® (22.5 mg), which is designed to release 22.5 mg of triptorelin over a 6-month period. Upon reaching the end of the first month of therapy, post-castration serum testosterone levels are maintained while the patient receives injections every 24 weeks.
This leads to additional atrophy of the penis. These effects are generally reversible upon discontinuation of drug therapy. Monitoring the effectiveness of therapy can be carried out by measuring the levels of testosterone in the blood serum and prostate-specific antigen (PSA). During the program of clinical studies for the 6th month of therapy with Diferelin (22.5 mg), a 97% relative decrease in median PSA levels was observed.
In experimental animal models, the use of triptorelin caused growth inhibition of some hormone-sensitive prostate tumors.
Clinical efficacy and safety in patients with prostate cancer
Administration of Diphereline® (22.5 mg) to patients with advanced prostate cancer by intramuscular injection for a total of 2 doses (12 months) resulted in both post-castration testosterone levels in 97.5% of patients after four weeks and maintenance of post-castration levels from 3.
Several randomized long-term clinical trials in patients with locally advanced prostate cancer have demonstrated the superiority of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) in combination with radiotherapy (RT) over RT (RTOG 85-31, RTOG 86-8JA-8 MA, 2008).
In a randomized phase III trial (EORTC 22961) of 970 patients with locally advanced prostate cancer (predominantly T2c-T4 and a few patients with T1C-T2B cancer with pathological regional nodal involvement), 483 with radiotherapy and 487 with long-term therapy (3 years), a lack of benefit analysis compared short-term and long-term concomitant and ancillary hormonal therapy with LHRH agonists, predominantly triptorelin (62.2%) or goserelin (30.1%).
Overall mortality at 5 years was 19.0% and 15.2%, respectively, in the short-term hormonal treatment and long-term hormonal treatment groups, with a relative risk of 1.42 (95% CI 71% = 1.79; or 95.71% CI = [1.09; 0.06; 0.06; 1.85; hoc).Prostate cancer-related mortality at 5 years was 4.78% and 3.2%, respectively, in the short-term hormonal treatment and long-term hormonal treatment groups, with a relative risk of 1.71 (95% CI [1.14 to 2.57], p = 0.002). Overall quality of life, as assessed using the QLQ-C30 questionnaire, did not differ significantly between the two groups (P = 0.37).
The evidence base for the use of this drug in the treatment of high-risk, localized prostate cancer is based on published studies of radiotherapy in combination with GnRH analogs. Clinical data from five published studies were analyzed (EORTC 22863, RTOG 85-31, RTOG 92-02, RTOG 86-10 and D’Amico et al., JAMA, 2008). They all demonstrated the benefit of combining therapy with a GnRH analogue and radiotherapy. Published studies do not allow a clear differentiation of relevant study populations between indications for locally advanced prostate cancer and high-risk localized prostate cancer. In patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, clinical studies have demonstrated the benefit of adding abiraterone acetate as an inhibitor of androgen biosynthesis or enzalutamide as an inhibitor of androgen receptor function to GnRH analogs, such as triptorelin.
Clinical efficacy and safety in children with precocious puberty
In a peer-to-peer clinical study, 44 children with central precocious puberty (39 girls and 5 boys) received a total of two intramuscular injections of Diphereline (22.5 mg) over a period of 12 months (48 weeks). Suppression of stimulated LH concentrations to prepubertal levels was achieved in 95.5% of patients up to month 3 and in 93.2% and 97.7% of patients up to months 6 and 12, respectively.
The therapy resulted in a regression or stabilization of minor sexual characteristics and a slowdown in accelerated bone maturation and growth.
In girls during the first month of treatment, initial ovarian stimulation followed by withdrawal of estrogen during treatment may result in low-to-moderate vaginal withdrawal bleeding.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption
After a single intramuscular injection of Diphereline in patients with prostate cancer, tmax (time to reach maximum concentration) was 3 (2-12) hours, and Cmax (maximum concentration) (0-169 days) was 40 (22.2-76.8) ng / ml. Triptorelin did not accumulate during 12 months of therapy.
Distribution
The results of pharmacokinetic studies conducted with the participation of healthy volunteers indicate that after intravenous bolus administration, the distribution and elimination of triptorelin proceed in accordance with a three-compartment model. The half-lives are approximately 6 minutes, 45 minutes and 3 hours, respectively.
The volume of distribution of triptorelin at steady state after administration of 0.5 mg of triptorelin acetate is approximately 30 liters in healthy male volunteers. Because there is no evidence of triptorelin binding to plasma proteins at clinically relevant concentrations, drug interactions, including substitution at binding sites, are unlikely.
Biotransformation
Triptorelin metabolites have not been found in humans. However, pharmacokinetic studies show that C-terminal fragments produced due to tissue breakdown are completely degraded within tissues and then rapidly degraded in blood plasma or eliminated by the kidneys.
Conclusion
Triptorelin is eliminated both through the liver and by the kidneys. After intravenous administration of 0.5 mg triptorelin in healthy male volunteers, 42% of the dose is excreted in the urine as intact triptorelin, the percentage rises to 62% in patients with impaired liver function. In healthy volunteers, creatinine clearance (Clcreat) was 150 ml/min and only 90 ml/min in patients with hepatic impairment. This indicates that the main site of elimination of triptorelin is the liver. In healthy volunteers, the actual terminal half-life was 2.8 hours and the total clearance of triptorelin was 212 ml/min. The latter indicator depends on the combination of hepatic and renal elimination.
Special populations of patients
With intravenous administration of 0.5 mg triptorelin in patients with moderate renal insufficiency (Clcreat 40 ml / min), the half-life of triptorelin was 6.7 hours and 7.81 hours in patients with severe renal insufficiency (Clcreat 8.9 ml / min / min) 9.9 ml / min).
A systematic study of the effect of age and race on pharmacokinetics has not been conducted. However, pharmacokinetic data obtained in young healthy male volunteers aged 20 to 22 years with elevated creatinine clearance (approximately 150 ml / min) showed that the elimination of triptorelin occurs 2 times faster in the young population. This is because triptorelin clearance correlates with total creatinine clearance, which is known to decrease with age.
Because triptorelin has a wide safety margin and Diphereline is a sustained-release drug, dose adjustment is not recommended during therapy in patients with impaired hepatic or renal function.
Pharmacokinetic / pharmacodynamic relationship
Evaluation of the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship of triptorelin is not easy due to the fact that the relationship is non-linear and time dependent. Thus, after the immediate use of previously untreated patients, triptorelin induces a dose-dependent increase in the response of LH and FSH.
When a slow-release drug is administered during the first days after dosing, triptorelin stimulates the secretion of LH and FSH and, as a consequence, the secretion of testosterone. As can be seen from the results of diverse bioequivalence studies, the maximum increase in testosterone levels is achieved within 4 days with an equivalent Cmax that is independent of the release rate of triptorelin. This initial response is not maintained despite continuous triptorelin exposure, followed by a progressive and equivalent decrease in testosterone levels. In this case, the degree of triptorelin exposure can also vary markedly, without changing the overall effect on serum testosterone levels.
Indications for use Diphereline 22.50 mg/ml solution for injection:
Treatment of locally advanced or metastatic hormone-dependent prostate cancer.
Treatment of high-risk localized or locally advanced prostate cancer in combination with radiotherapy.
Treatment of precocious puberty of central origin in children from 2 years of age (in girls under 8 years of age and in boys under 10 years of age).
Contraindications for use Diphereline 22.50 mg/ml solution for injection:
Hypersensitivity to GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone), its analogues or any excipients of the drug.
The period of pregnancy and lactation.
Interaction with other medicinal products:
When using triptorelin together with drugs that modify the secretion of pituitary gonadotropic hormones, precautions must be taken, and careful monitoring of the patient’s hormonal levels is recommended.
Since androgen deprivation therapy may prolong the QT interval, concomitant use of Diphereline® (22.5 mg) with drugs that prolong the QT interval or can cause torsades de pointes, such as class AI antiarrhythmics (quinidine, class, disopyr ibutilide), as well as methadone, cisapride, moxifloxacin, antipsychotics require careful evaluation ( see section “Application features”).
Children
Interaction studies have only been conducted in adults.
Precautions & Warning for use Diphereline 11,25 mg/ml solution for injection:
The use of GnRH agonists can cause a decrease in bone mineral density. Preliminary evidence suggests that in men, the use of a bisphosphonate together with a GnRH agonist may reduce bone mineral density loss. Particular attention should be given to patients with additional risk factors for osteoporosis (such as alcohol abuse, smoking, long-term treatment with drugs that cause a decrease in bone mineral density, such as anticonvulsants or corticosteroids, a hereditary predisposition to osteoporosis), insufficiency.
In rare cases, therapy with GnRH agonists can reveal a previously undiagnosed gonadotropic pituitary adenoma. Such patients may present with pituitary apoplexy, characterized by sudden headaches, vomiting, visual disturbances, and ophthalmoplegia.
There is an increased risk of depression (which can be severe) in patients treated with GnRH agonists, in particular triptorelin. With this in mind, patients should be informed and provided with appropriate treatment when symptoms appear.
Patients who are depressed need careful monitoring during therapy.
Intramuscular injections should be used with caution in patients treated with anticoagulants due to the risk of hematomas at the injection site. The efficacy and safety of Diphereline (22.5 mg) has been demonstrated only when administered intramuscularly.
Subcutaneous administration of this medicinal product is not recommended.
Diphereline® (22.5 mg) contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) sodium per dose, i.e. it is generally sodium-free.
Prostate cancer
Initially, triptorelin therapy, like other GnRH agonists, results in a transient increase in serum testosterone levels. As a result, isolated cases of temporary worsening of prostate cancer symptoms may develop during the first weeks of treatment. During the initial phase of treatment, consideration should be given to the addition of an appropriate antiandrogen to counteract the initial increase in serum testosterone levels and prevent worsening of clinical symptoms.
A minority of patients may experience a temporary worsening of prostate cancer symptoms and a temporary increase in cancer-related pain (metastatic pain), which is treated symptomatically.
As with other GnRH agonists, isolated cases of spinal cord compression or urethral obstruction have been observed. With the development of spinal cord compression or impaired renal function, standard methods of treatment of these complications are used, and in emergency cases, the possibility of immediate orchiectomy (surgical castration) is considered. In the first weeks of treatment, careful monitoring is indicated, especially in patients with vertebral metastases, at risk of spinal cord compression and/or patients with urinary tract obstruction. After surgical castration, triptorelin does not induce any further decrease in serum testosterone levels. Once post-castration testosterone levels are reached at the end of the first month of therapy, serum testosterone levels are maintained while the patient receives injections every 6 months (twenty-four weeks).
Monitoring the effectiveness of therapy can be carried out by measuring the levels of testosterone in the blood serum and prostate-specific antigen (PSA).
Long-term androgen loss due to bilateral orchiectomy or GnRH analogues is associated with an increased risk of bone loss and may lead to osteoporosis and an increased risk of bone fractures.
Androgen deprivation therapy may cause QT interval prolongation.
In patients with a history of prolongation of the QT interval or with existing risk factors for prolongation of the QT interval, as well as in patients receiving drugs that can prolong the QT interval (see the section “Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction), the benefit-to-risk ratio, including the potential for occurrence, should be assessed. Ellinom® (22.5 mg).
In addition, in view of epidemiological data, it was noted that patients may have metabolic changes (for example, glucose intolerance) or an increased risk of cardiovascular disease during antiandrogen therapy. However, prospective data do not support an association between GnRH analog therapy and increased cardiovascular mortality. Before starting therapy, patients with a high risk of metabolic or cardiovascular diseases should be carefully examined and appropriately monitored during antiandrogen therapy.
The introduction of triptorelin in therapeutic doses leads to suppression of the pituitary-gonadal system. After discontinuation of treatment, restoration of normal system function is usually observed. Thus, the results of diagnostic tests of the pituitary-gonadal system, performed during treatment and after cessation of therapy with GnRH analogues, may be false.
Precocious puberty
Before starting treatment for children with advanced brain tumors, the risks and benefits should be carefully assessed in each individual case.
Pseudo-premature puberty (tumors of the genital or adrenal glands or hyperplasia) and gonadotropin-independent precocious puberty (testicular intoxication, hereditary Leydig cell hyperplasia) should be excluded in advance.
In girls during the first month of treatment, initial ovarian stimulation followed by estrogen withdrawal during treatment may result in low to moderate vaginal bleeding.
Therapy is long, adjusted individually. Diphereline (22.5 mg) should be used with strict observance of the interval between injections – 6 months. In exceptional circumstances, delaying the injection by several days (169 ± 3 days) does not affect the results of treatment.
After completion of therapy, signs of puberty develop.
Future fertility data are limited, but GnRH treatment is unlikely to affect future reproductive function and fertility. For most girls, regular periods begin an average of one year after completion of treatment.
In the treatment of central precocious puberty with GnRH agonists, bone mineral density may decrease, given the expected effects of estrogen suppression. However, after treatment is stopped, further accumulation of bone mass occurs, and maximum bone mass in late puberty is not affected by treatment.
After discontinuation of treatment with GnRH agonists, epiphysiolysis of the femoral head may develop. There is a theory that the low concentration of estrogen during treatment with GnRH agonists weakens the epiphyseal plate. Acceleration of growth after completion of treatment leads to a decrease in the displacement force required to displace the epiphysis.
Use during pregnancy or lactation
Pregnancy
Diphereline (22.5 mg) is indicated for use in adult men and children. Data on the use of triptorelin in pregnant women are too limited. Diphereline (22.5 mg) is not indicated for use in women.
Before starting treatment with Diferelin (22.5 mg), a woman should be excluded from the possibility of pregnancy.
Triptorelin is contraindicated during pregnancy, as the concomitant use of GnRH agonists is associated with a theoretical risk of abortion or malformations in the child. Before starting treatment, potentially fertile women should undergo a thorough examination to exclude the possibility of pregnancy. During treatment and until the restoration of menstruation, non-hormonal methods of contraception should be used.
Animal studies have shown an effect on reproductive parameters.
Lactation
Diphereline (22.5 mg) is contraindicated during lactation.
The ability to influence the reaction rate when driving vehicles or operating other mechanisms
Studies of the effect on the reaction rate when driving vehicles or operating other mechanisms have not been conducted. However, the ability to drive vehicles and operate other mechanisms may be impaired due to dizziness, drowsiness and visual disturbances, which may be undesirable effects of therapy or the result of a concomitant disease.
Side Effects:
General tolerance in men
Due to the fact that patients with locally advanced or metastatic hormone-dependent prostate cancer are usually elderly and have other diseases that are common in patients in this age group, more than 90% of patients who participated in clinical studies experienced adverse events and were often difficult to assess. Based on treatment with other GnRH agonists or after surgical castration, the most frequently observed adverse reactions associated with triptorelin therapy were due to the expected pharmacological action. These effects included hot flashes and decreased sex drive.
With the exception of immunoallergic reactions (rare) and reactions at the injection site (< 5%), all adverse events are known to be related to changes in testosterone levels.
The following adverse reactions have been reported and considered at least likely to be related to triptorelin therapy. The occurrence of most of these phenomena is associated with biochemical or surgical castration.
In patients undergoing therapy with GnRH analogues, an increase in the number of lymphocytes is observed. This secondary lymphocytosis is likely related to GnRH-induced castration and suggests that gonadal hormones are most likely involved in thymic involution.
Interaction:
When using triptorelin together with drugs that modify the secretion of pituitary gonadotropic hormones, precautions must be taken, and careful monitoring of the patient’s hormonal levels is recommended.
Since androgen deprivation therapy may prolong the QT interval, concomitant use of Diphereline® (22.5 mg) with drugs that prolong the QT interval or can cause torsades de pointes, such as class AI antiarrhythmics (quinidine, class, disopyr ibutilide), as well as methadone, cisapride, moxifloxacin, antipsychotics require careful evaluation.
Children
Interaction studies have only been conducted in adults.
Overdose:
Given the pharmaceutical properties of Diphereline®, as well as the method of its administration, the possibility of an overdose is unlikely. There are no data on overdose in humans. In case of overdose, symptomatic treatment is recommended.
Storage:
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life:
2 year.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.