Description
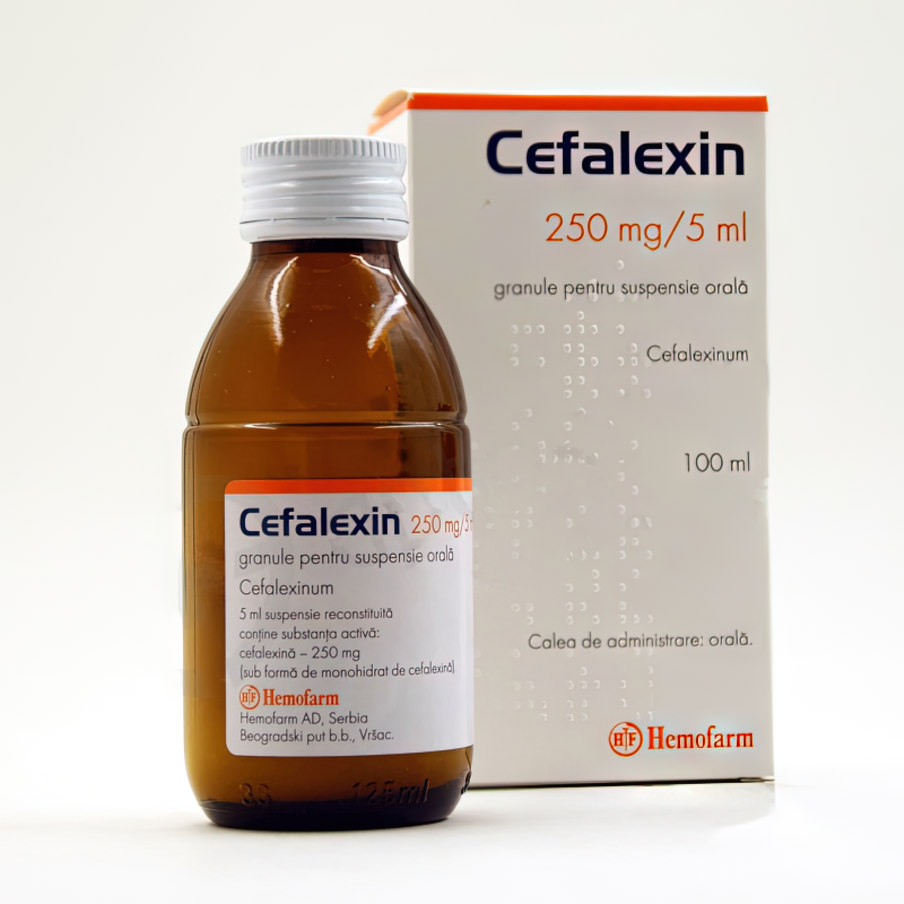
Buy Cefalexin 250 mg/5 ml 100 ml powder for oral suspension
Description of Cefalexin 250 mg / 5 ml powder for oral suspension:
Granules for oral suspension.
Basic physical and chemical properties: yellow-orange granular powder. When the recommended amount of water is added, a yellow ocher suspension with a characteristic fruity odor and a bittersweet taste is formed.
Cefalexin is an antibiotic used to treat infections in different parts of the body caused by bacteria.
Cefalexin belongs to a group of antibiotics called cefalosporins. These antibiotics work by killing the bacteria that are causing your infection.
Ingredients:
Active ingredient: cefalexin;
5 ml of the finished suspension contains cefalexin 250 mg in the form of cefalexin monohydrate;
Other ingredients: sodium saccharin, anhydrous citric acid, iron oxide yellow (E 172), guar gum, sodium benzoate (E 211), simethicone, sucrose, aromas: strawberry, apple, raspberry, tutti frutti.
Pharmacological Properties of Cefalexin 250 mg / 5 ml powder for oral suspension:
Pharmacodynamics.
Cefalexin is a semi-synthetic broad-spectrum antibiotic. Gram-positive microorganisms are sensitive to cephalexin: staphylococci (coagulase-positive and penicillin-producing strains), streptococci (with the exception of enterococci), pneumococci. Cefalexin also acts on Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., Proteus mirabilis.
Cefalexin is inactive against Enterococcus spp., Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-resistant), Enterobacter spp., Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Mycoplasma spp., Chlamydia spp.
Pharmacokinetics.
Cefalexin is rapidly and almost completely absorbed after oral administration (more than 90%). The level and rate of absorption of cefalexin are practically independent of food intake. Peak serum concentrations are reached 60-90 minutes after taking the drug. Cefalexin penetrates well into tissues and body fluids, including pericardial and pleural membranes. Only 10-15% of the active substance binds to plasma proteins. The drug is excreted mainly in the urine unchanged. Cefalexin is excreted by hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Indications of Cefalexin 250 mg / 5 ml powder for oral suspension:
Treatment of infections caused by microorganisms sensitive to cefalexin:
- ENT organs and respiratory tract (pharyngitis, otitis media, sinusitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia);
- genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis, epididymitis, endometritis, vulvovaginitis);
- skin and soft tissues (furunculosis, abscess, phlegmon, pyoderma, lymphadenitis);
- bone tissue and joints (osteomyelitis).
Precautions of Cefalexin 250 mg / 5 ml powder for oral suspension:
Before starting therapy, a history of hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins, penicillins or other allergens should be determined.
There is a possibility of cross-allergic reactions between penicillins and cephalosporins.
(5-10%). Severe hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis) have been reported with both drugs.
Cefalexin should be used with caution in patients with a tendency to allergic diseases (hay fever, allergic diathesis) and / or with bronchial asthma.
Prolonged use of cefalexin can lead to dysbacteriosis and superinfection (candidiasis).
If a secondary infection occurs, precautions should be taken.
During treatment, the cellular composition of peripheral blood, liver and kidney function should be regularly monitored.
Cefalexin should be used with caution in patients with severely impaired renal function. It is recommended to regularly monitor kidney function and adjust the dose.
With the use of almost all broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs, including macrolides, semi-synthetic penicillins, cephalosporins, it is possible to develop pseudomembranous colitis from mild to life-threatening. Therefore, if diarrhea occurs after the use of antimicrobial agents, it is important to make sure that it is not associated with this pathology.
If severe diarrhea occurs, characteristic of pseudomembranous colitis, it is recommended to stop using the drug and take appropriate measures. The use of agents that inhibit peristalsis is contraindicated.
Treatment with cephalosporins (including cephalexin) may be associated with a decrease in prothrombin activity, therefore, in patients with impaired synthesis or deficiency of vitamin K (for example, in patients with chronic liver disease, kidney disease, cystic fibrosis, elderly patients, patients who are malnourished, patients on agulants prior to the appointment of cephalexin, prothrombin time should be monitored and, if necessary, vitamin K should be prescribed to them.
The drug contains sucrose, so if you have an intolerance to some sugars, consult your doctor before taking this medicine.
A positive result has been reported in the direct Coombs test when treated with cephalosporin antibiotics. A positive Coombs test result can be observed in newborns whose mothers took cephalexin during pregnancy.
When determining the level of glucose in the urine when using the drug, a glucose oxidase test should be used, since other methods (Fehling or Benedict tests) may give false positive results.
Cephalosporins may interfere with urine tests for the presence of ketone bodies.
Use during pregnancy and lactation.
There are no data from studies on the teratogenic effect of the drug; during pregnancy, it can be prescribed only after a thorough assessment of the benefit/risk ratio.
Cefalexin passes into breast milk, so during the period of treatment it is advisable to stop breastfeeding.
The ability to influence the reaction rate when driving vehicles or operating other mechanisms.
Until an individual reaction to the drug is clarified (dizziness, confusion may occur), it is recommended to be careful when driving vehicles or operating other mechanisms.
Interactions of Cefalexin 250 mg / 5 ml powder for oral suspension:
Given the bactericidal effect of cefalexin, it should not be combined with bacteriostatic antibiotics, such as tetracyclines and chloramphenicol.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: the excretion of cefalexin slows down.
When combined with highly active diuretics (ethacrynic acid, furosemide) or potentially nephrotoxic drugs (aminoglycosides, polymyxin, colistin, amphotericin, capreomycin, vancomycin), cephalosporins may increase nephrotoxicity.
Drugs that reduce platelet aggregation (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antiplatelet agents, vitamin K antagonists (such as warfarin), sulfinpyrazone) prolong prothrombin time and increase the risk of bleeding.
Probenecid, phenylbutazone reduce the renal excretion of cefalexin, as well as other beta-lactam drugs.
Simultaneous use with probenicide or phenylbutazone may lead to an increase in the half-life and plasma concentrations of cefalexin.
Cephalosporins may reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives, so the use of additional contraceptives is recommended.
The interaction of cephalexin and metformin can lead to the accumulation of metformin. With the simultaneous use of cefalexin and metformin in a single dose of 500 mg, Cmax and AUC of metformin increase by an average of 34 and 24%, respectively, and renal clearance decreases by 14%.
Patients taking cytotoxic drugs for leukemia may develop hypokalemia while using gentamicin and cefalexin.
Side effects of Cefalexin 250 mg / 5 ml powder for oral suspension:
On the part of the digestive tract: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cramps / pain in the abdomen, loss of appetite / anorexia (generally disappears spontaneously even with continued use of the drug), dry mouth, dyspepsia, flatulence, gastritis, rarely – colitis, including pseudo. iasis, candidiasis stomatitis, intestinal candidiasis, anal itching.
From the hepatobiliary system: a transient increase in the activity of hepatic transaminases (aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and alkaline phosphatase, plasma bilirubin levels, transient toxic hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice.
From the blood system: neutropenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia / thrombocytosis, eosinophilia, agranulocytosis, lymphopenia, pancytopenia, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, prolongation of prothrombin time, hemorrhages.
From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions, incl. allergic reactions in patients with identified allergy to penicillins, cephalosporins; angioedema, rarely – anaphylaxis (including bronchospasm, shortness of breath, decreased blood pressure, anaphylactic shock), anaphylactoid reactions, drug-induced fever. Usually, allergic reactions disappear after cessation of therapy.
On the part of the skin and subcutaneous tissue: skin rash, including erythematous, dermatitis, itching, skin flushing, urticaria, edema, incl. face and / or neck, hands and / or feet, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
From the nervous system: dizziness, vertigo, weakness, headaches, agitation, confusion, hallucinations, convulsive seizures are possible (especially in patients with renal insufficiency against the background of an uncorrected dosage).
From the genitourinary system: very rarely – reversible renal dysfunction, possible manifestations of toxic nephropathy in patients with impaired renal function, isolated cases of interstitial nephritis. Reversible fever, elevated blood urea nitrogen, hypercreatininemia, pyuria, and eosinophiluria are characteristic features of cephalosporin-induced interstitial nephritis. Acute tubular necrosis has also been reported.
From the musculoskeletal system: joint damage, arthralgia, arthritis.
From the reproductive system: genital candidiasis, genital itching, vaginitis, vaginal discharge.
Others: increased fatigue, increased levels of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the blood serum, false positive Coombs test, false positive result in the study of urine for sugar.
Overdose:
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, diarrhea, hematuria, electrolyte imbalance, hyperreflexia, convulsions.
Excitement: in case of overdose, clinical and laboratory monitoring of hematological, renal, hepatic functions and blood coagulation is necessary until the patient’s condition stabilizes.
Gastric lavage should be carried out when the usual dose is exceeded by 5-10 times.
Symptomatic treatment is used (activated charcoal, hemodialysis).
Storage:
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 C, in the original packaging to protect from light and moisture. After preparation, store the suspension at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C for 14 days.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life:
3 year.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.