Description
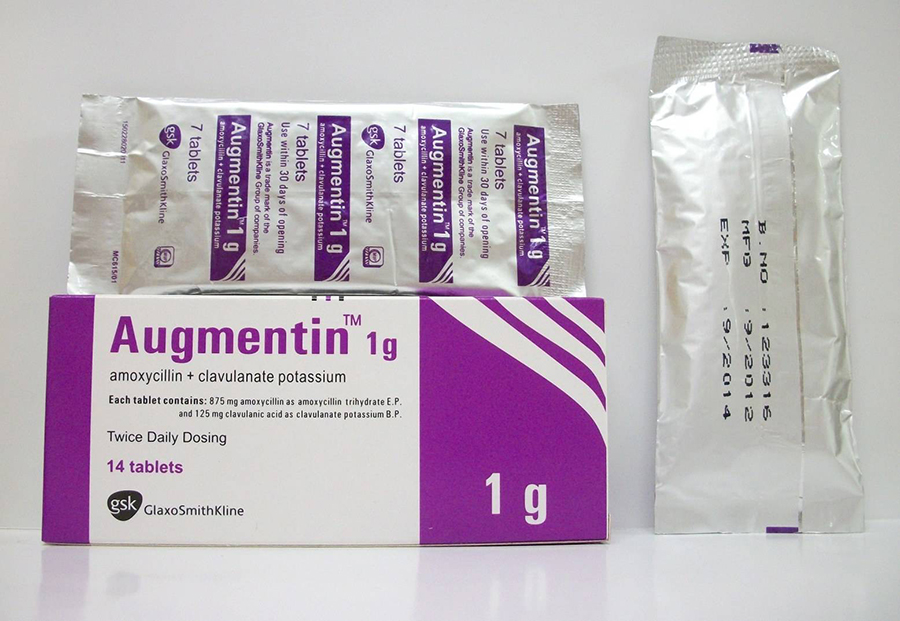
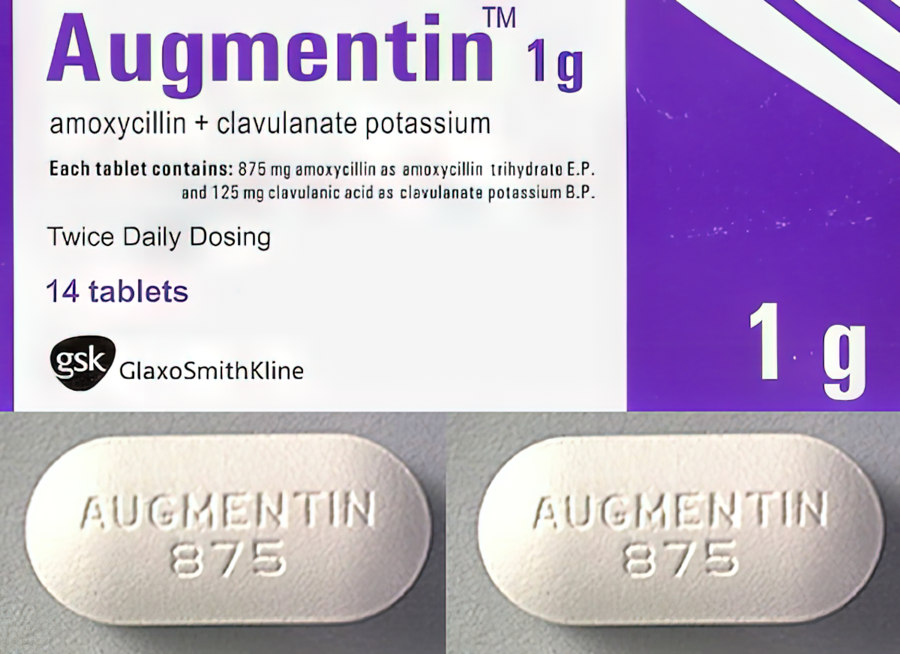
Buy Augmentin BD 1000 mg tablets
Description of Augmentin BD 1000 mg tablets:
Active ingredients: amoxicillin and clavulanic acid.
Amoxicillin is an analog of ampicillin, derived from the basic penicillin nucleus, 6-aminopenicillanic acid Clavulanic acid is produced by the fermentation of Streptomyces clavuligerus. It is a beta-lactam structurally related to the penicillins and possesses the ability to inactivate some beta-lactamases by blocking the active sites of these enzymes. Lower Respiratory Tract Infections – caused by beta-lactamase-producing isolates of Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis. Acute Bacterial Otitis Media – caused by beta-lactamase-producing isolates of H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis. Sinusitis – caused by beta-lactamase-producing isolates of H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis. Skin and Skin Structure Infections – caused by beta-lactamase-producing isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella species. Urinary Tract Infections – caused by beta-lactamase-producing isolates of E. coli, Klebsiella species, and Enterobacter species.
Ingredients:
1 tablet contains amoxicillin (in the form of amoxicillin trihydrate) 875 mg, clavulanic acid (in the form of clavulanate potassium) 125 mg;
excipients: magnesium stearate, sodium starch glycolate (type A), anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide, microcrystalline cellulose, dimethicone;
tablet shell: titanium dioxide (E 171), hypromelose (5 cps), hypromelose (15 cps), macrogol 4000, macrogol 6000.
Pharmacologic effect of Augmentin BD 1000 mg tablets:
Mechanism of action
Amoxicillin is a semi-synthetic penicillin (beta-lactam antibiotic) that inhibits one or more enzymes (often referred to as penicillin-binding proteins, PBPs) in the biosynthetic metabolism of bacterial peptidoglycan, which is an integral structural component of cell walls. Inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis leads to weakening of the cell wall, resulting in cell lysis and death.
Amoxicillin is sensitive to degradation by beta-lactamases produced by resistant bacteria, therefore, the spectrum of activity of amoxicillin as monotherapy does not include microorganisms that produce these enzymes.
Clavulanic acid is a beta-lactam structurally related to penicillins. It deactivates some beta-lactamase enzymes, thereby preventing the inactivation of amoxicillin. Clavulanic acid alone does not provide a clinically useful antibacterial effect.
Pharmacokinetics of Augmentin BD 1000 mg tablets:
Suction
Absorption. Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid completely dissociate in aqueous solution at physiological pH. Both components are rapidly and well absorbed when taken orally. The bioavailability of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid is about 70% when taken orally. The plasma profiles of both components are identical, and the time to reach maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) for each component is approximately one hour.
Serum concentrations of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid achieved with the amoxicillin/clavulanic acid combination are identical to those achieved with oral administration of equivalent doses of amoxicillin or clavulanic acid alone.
Distribution. About 25% of the total clavulanic acid in plasma and 18% of the total amoxicillin in plasma are protein bound. The volume of distribution is about 0.3–0.4 L/kg for amoxicillin and about 0.2 L/kg for clavulanic acid.
Following intravenous administration, amoxicillin and clavulanic acid have been found in the gallbladder, peritoneum, skin, adipose tissue, muscle tissue, synovial and peritoneal fluid, bile, and pus. Amoxicillin is not distributed sufficiently in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Animal studies have not revealed any evidence of significant retention of substances derived from any component of the drug in body tissues. Amoxicillin, like most penicillins, can be found in breast milk. A small amount of clavulanic acid can also be found in breast milk.
Both amoxicillin and clavulanic acid have been found to cross the placental barrier.
Biotransformation. Amoxicillin is partially excreted in the urine as inactive penicilloid acid in amounts equivalent to 10-25% of the initial dose. Clavulanic acid is largely metabolized in the human body and excreted in urine and feces and as carbon dioxide in exhaled air.
Withdrawal. The main route of excretion of amoxicillin is the kidneys, while clavulanic acid is excreted both by the kidneys and by the action of extrarenal mechanisms.
In healthy volunteers, the mean half-life of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid is approximately one hour and the mean total clearance is approximately 25 L/h. Various studies have shown that urinary excretion is 50-85% for amoxicillin and 27-60% for clavulanic acid over a 24-hour period. The greatest amount of clavulanic acid is excreted during the first 2 hours after ingestion.
The simultaneous use of probenecid slows down the excretion of amoxicillin, but does not delay the renal excretion of clavulanic acid.
Age. The half-life of amoxicillin is identical for children 3 months to 2 years of age, older children and adults. Since elderly patients are more prone to decreased renal function, dosage should be selected with caution, and monitoring of renal function is also recommended.
Impaired kidney function. The total serum clearance of amoxicillin / clavulanic acid decreases proportionally with a decrease in renal function. The decrease in drug clearance is more pronounced for amoxicillin than for clavulanic acid, since most of the amoxicillin is excreted by the kidneys. In renal insufficiency, the dosage should prevent excessive accumulation of amoxicillin while maintaining sufficient levels of clavulanic acid.
Impaired liver function. Patients with hepatic insufficiency are advised to carefully use the drug and regularly monitor liver function.
Indications for use of Augmentin BD 1000 mg tablets:
Treatment in adults and children of bacterial infections caused by microorganisms sensitive to Augmentin, such as:
Usually sensitive species:
- Gram-positive aerobes: Enterococcus faecalis, Gardnerella vaginalis, Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-sensitive), coagulase-negative staphylococcus (methicillin-sensitive), Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae1, Streptococcus pyogenes and other beta-hemolytic streptococci, group Streptococcus virid;
- Gram-negative aerobes: Capnocytophaga spp., Eikenella corrodens, Haemophilus influenzae2, Moraxella catarrhalis, Pasteurella multocida;
- Anaerobes: Bacteroides fragilis, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Prevotella spp.
Bacterial infections caused by microorganisms sensitive to Augmentin:
- acute bacterial sinusitis (confirmed);
- acute otitis media;
- confirmed exacerbation of chronic bronchitis;
- community-acquired pneumonia;
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis;
- infections of the skin and soft tissues, including cellulitis, animal bites, severe odontogenic abscesses with cellulitis;
- bone and joint infections, incl. osteomyelitis.
Infections caused by microorganisms sensitive to amoxicillin can be treated with the AUGMENTIN drug, since amoxicillin is one of its active substances.
The AUGMENTIN drug is also indicated for the treatment of mixed infections caused by microorganisms that are sensitive to amoxicillin, as well as microorganisms producing β-lactamase that are sensitive to a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid.
Contraindications for use Augmentin BD 1000 mg tablets:
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, to any antibacterial agents of the penicillin group.
A history of severe hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis) associated with the use of other β-lactam agents (including cephalosporins, carbapenems, or monobactams).
A history of jaundice or liver dysfunction, associated with the use of amoxicillin/clavulanate.
Precautions:
- Before starting therapy with amoxicillin / clavulanic acid, information should be carefully collected on prior hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins or other beta-lactam drugs;
- Serious and in some cases fatal hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylactic reactions and severe skin adverse reactions) have been reported in patients treated with penicillin. Such reactions are more likely in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to penicillin and patients with atopic diseases. If an allergic reaction occurs, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid should be discontinued and appropriate alternative therapy instituted;
- If the infection is proven to be caused by an amoxicillin-susceptible microorganism(s), consideration should be given to switching from amoxicillin/clavulanic acid to amoxicillin in accordance with generally accepted guidelines;
- This dosage form of Augmentin should not be used if there is a high risk that possible pathogens have reduced sensitivity or resistance to beta-lactam drugs, which is not mediated by beta-lactamases sensitive to clavulanic acid inhibition. For the treatment of patients whose disease is caused by penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae, this dosage form should not be used;
- If the infection is proven to be caused by an amoxicillin-susceptible microorganism(s), consideration should be given to switching from amoxicillin/clavulanic acid to amoxicillin in accordance with generally accepted guidelines;
- This dosage form of Augmentin should not be used if there is a high risk that possible pathogens have reduced sensitivity or resistance to beta-lactam drugs, which is not mediated by beta-lactamases sensitive to clavulanic acid inhibition. For the treatment of patients whose disease is caused by penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae, this dosage form should not be used;
- Amoxicillin / clavulanic acid should be used with caution in patients with evidence of hepatic impairment.
Interactions:
Simultaneous use of allopurinol in the treatment of amoxicillin increases the likelihood of allergic reactions from the skin.
Oral anticoagulants: Oral anticoagulants and penicillin antibiotics are widely used in practice without interaction reports. However, cases of an increase in the international coefficient of normalization in patients taking acenocoumarol or warfarin, and who were prescribed a course of treatment with amoxicillin, have been described.
Methotrexate: Penicillins can reduce the excretion of methotrexate, which causes a potential increase in toxicity.
Probenecid: Co-administration of probenecid is not recommended. Probenecid reduces the renal tubular secretion of amoxicillin. Simultaneous use of probenecid may lead to an increase in the level and duration of amoxicillin (but not clavulanic acid) in the blood.
Mycophenolate mofetil: In patients treated with mycophenolate mofetil, after initiation of oral amoxicillin with clavulanic acid, the predose concentration of the active metabolite, mycophenolic acid, may decrease by approximately 50%. This change in pre-dose level may be consistent with the change in total exposure to mycophenolic acid. Thus, a change in the dosage of mycophenolate mofetil is usually not required unless there is clinical evidence of graft dysfunction. However, close monitoring is necessary during concomitant use and for some time after antibiotic therapy.
Side effects:
The most frequently reported adverse reactions to the drug were diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
The list of adverse reactions to the drug known from clinical studies of Augmentin and post-registration surveillance and classified according to the MedDRA system organ class is listed below:
Infections and invasions.
Often: candidiasis of the skin and mucous membranes.
Not known: overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms.
From the hematopoietic and lymphatic system.
Rare: reversible leukopenia (including neutropenia) and thrombocytopenia.
Not known: reversible agranulocytosis and hemolytic anemia; increase in bleeding time and prothrombin index1.
From the side of the immune system10.
Not known: angioedema, anaphylaxis, serum sickness-like syndrome, allergic vasculitis.
From the side of the nervous system.
Uncommon: dizziness, headaches.
Not known: reversible hyperactivity and seizures2.
Not known: aseptic meningitis.
From the gastrointestinal tract.
Very common: diarrhea.
Often: nausea 3, vomiting.
Uncommon: indigestion.
Not known: antibiotic-associated colitis 4, black hairy tongue.
Hepatobiliary disorders.
Infrequently: increased levels of AST and / or ALT 5.
Not known: hepatitis6 and cholestatic jaundice6.
From the side of the skin and subcutaneous tissues 7.
Uncommon: skin rash, itching, urticaria.
Rare: erythema multiforme.
Not known: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, bullous exfoliative dermatitis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis9, drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
From the side of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Not known: interstitial nephritis, crystalluria 8.
Nausea is more commonly associated with higher oral doses of the drug. If gastrointestinal reactions occur, their severity may be reduced by taking Augmentin with meals.
Including pseudomembranous colitis and hemorrhagic colitis.
Moderate elevations in AST and/or ALT levels were more common in patients treated with beta-lactam antibiotics, but the significance of these findings is unknown.
These phenomena were observed with the use of other antibiotics of the penicillin and cephalosporin series.
If hypersensitivity reactions (dermatitis) occur, the drug should be discontinued.
Overdose of Augmentin BD 1000 mg tablets:
Symptoms
Symptoms consistent with gastrointestinal upset and fluid and electrolyte imbalances may be observed. Crystalluria associated with the use of amoxicillin was observed, which in rare cases led to the development of renal failure.
Convulsions may occur in patients with impaired renal function and in patients taking high doses.
Sedimentation of amoxicillin in bladder catheters has been reported, predominantly after administration at high doses. You should regularly check the patency of catheters.
Treatment
Gastrointestinal disorders can be treated symptomatically with attention to fluid/electrolyte balance.
Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid can be removed from the bloodstream by hemodialysis.
Storage:
Store below 25°C in original packaging. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life:
3 years.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.